The composition and usage characteristics of glass bottles
12-19-2023
Firstly, it is necessary to design, determine, and manufacture a mold. The glass raw material is mainly quartz sand, and other auxiliary materials dissolve into a liquid state at high temperatures. Then, it is injected into the mold, cooled, cut, and tempered to form a glass bottle. The molding of glass bottles can be divided into three types according to the production method: manual blowing, mechanical blowing, and extrusion molding. Glass bottles can be divided into the following types according to their composition: sodium calcium glass, lead glass, and borosilicate glass.
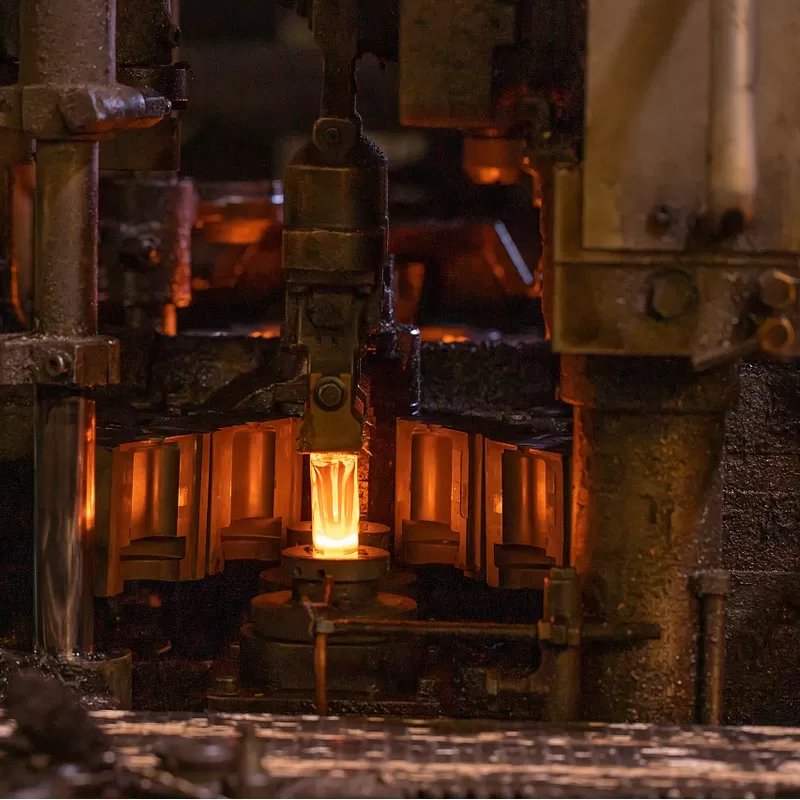

The main raw materials for glass bottles are natural ore, quartz, caustic soda, limestone, etc. Glass bottles have high transparency and corrosion resistance, and do not undergo changes in material properties when in contact with most chemicals. Its manufacturing process is simple, the shape is flexible and variable, the hardness is high, it is heat-resistant, clean, easy to clean, and has the characteristics of being reusable. Glass bottles, as packaging materials, are mainly used in food, oil, alcohol, beverages, seasonings, cosmetics, and liquid chemical products, and have a wide range of uses. But glass bottles also have their drawbacks, such as high weight, high transportation and storage costs, and lack of impact resistance.
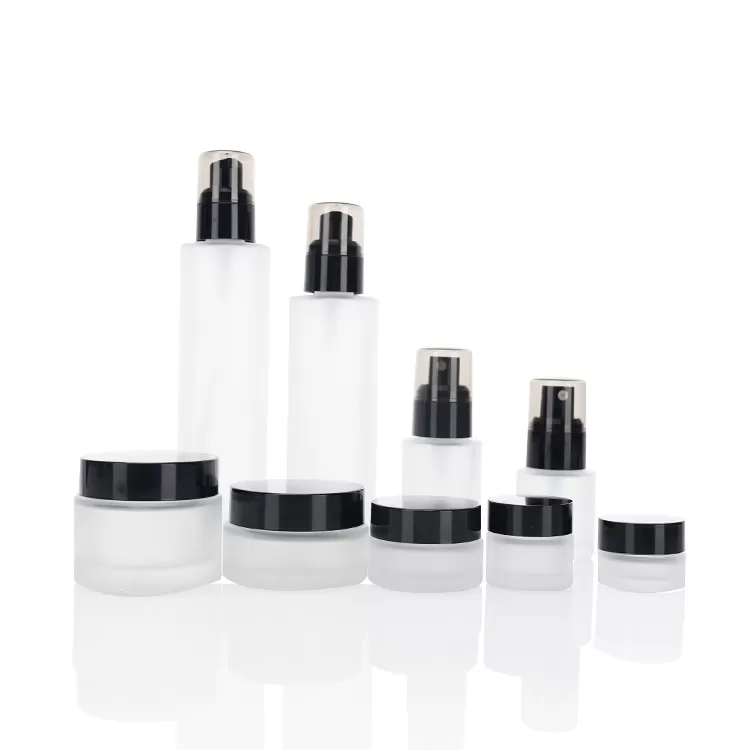

The usage characteristics and types of glass bottles: Glass bottles are the main packaging containers in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. They have good chemical stability; Easy to seal, good airtightness, transparent, and the condition of the contents can be observed from the outside; Good storage performance; Smooth surface for easy disinfection and sterilization; Beautiful appearance, rich and colorful decoration; Has a certain mechanical strength and can withstand the pressure inside the bottle and external forces during transportation; The advantages of wide distribution of raw materials and low prices. Its disadvantages are high quality (mass to capacity ratio), high brittleness, and fragility. However, in recent years, new technologies such as thin-walled lightweight and physical chemical tempering have been adopted, and these shortcomings have been significantly improved. Therefore, glass bottles can increase their production year by year in fierce competition with plastic, porcelain, and iron cans.
There are a wide variety of glass bottles, from small bottles with a capacity of 1ML to large bottles with a capacity of over ten liters, from round, square, to shaped and handled bottles, from colorless and transparent amber, green, blue, black opaque bottles, and opaque opaque glass bottles, to name a few. In terms of manufacturing technology, glass bottles are generally divided into two categories: molded bottles (using model bottles) and tube bottles (using glass tube bottles). Molded bottles are divided into two categories: large necked bottles (with a mouth diameter of over 30MM) and small necked bottles. The former is used to hold powdered, block like, and paste like items, while the latter is used to hold liquids. According to the form of bottle mouth, it can be divided into cork cork bottle mouth, threaded bottle mouth, crown cap bottle mouth, rolled and frosted bottle mouth, etc. According to usage, it can be divided into "disposable bottles" that are discarded once and "recycled bottles" that are reused multiple times. According to the classification of contents, it can be divided into wine bottles, beverage bottles, oil bottles, can head bottles, acid bottles, medicine bottles, reagent bottles, infusion bottles, cosmetic bottles, etc